Reversal of Oxidative Stress Through Anti-oxidation with Hydrogen Inhalation
Free radicals are unstable atoms that can damage cells, causing aging and is linked to a host of degenerative conditions and diseases.
What are free radicals?

The Negative Effects of Free Radicals
Free radicals are thought to be responsible for age-related changes in appearance, such as wrinkles and grey hair. Understanding free radicals requires a basic knowledge of chemistry. Atoms are surrounded by electrons that orbit the atom in layers called shells. Each shell needs to be filled by a set number of electrons. When a shell is full; electrons begin filling the next shell.
If an atom has an outer shell that is not full, it may bond with another atom, using the electrons to complete its outer shell. These types of atoms are known as Free Radicals. Atoms with a full outer shell are stable, but free radicals are unstable and in an effort to make up the number of electrons in their outer shell, they react quickly with other substances.
When oxygen molecules split into single atoms that have unpaired electrons, they become unstable free radicals that seek other atoms or molecules to bond to. If this continues to happen, it begins a process called Oxidative Stress. This can damage the body’s cells, leading to a range of diseases and causes symptoms of aging, such as wrinkles.
How do Free Radicals damage the body?

Free radicals are unstable atoms. To become more stable, they take electrons from other atoms. This may cause diseases or signs of aging. According to the free radical theory of aging, first outlined in 1956, free radicals break cells down over time. As the body ages, it loses its ability to fight the effects of free radicals. The result is more free radicals, more oxidative stress, and more damage to cells, which leads to degenerative processes, as well as ‘healthy’ aging.
Various studies and theories have connected oxidative stress due to free radicals to:
- central nervous system diseases, such as Alzheimer’s and other dementias
- cardiovascular disease due to clogged arteries
- autoimmune and inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis and cancer
- cataracts and age-related vision decline
- age-related changes in appearance, such as loss of skin elasticity, wrinkles, greying hair, hair loss, and changes in hair texture
- diabetes
- genetic degenerative diseases, such as Huntington’s disease or Parkinson’s
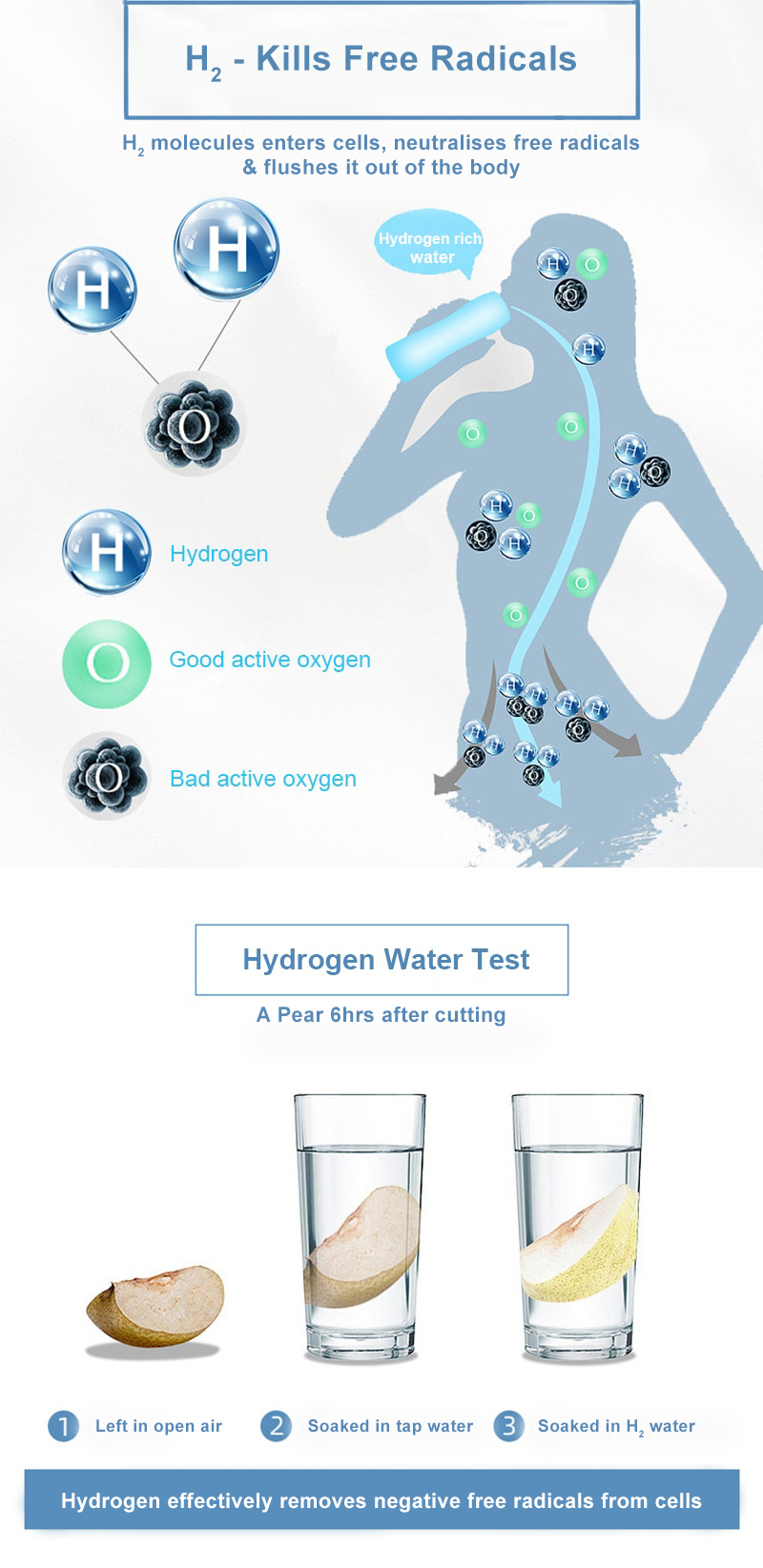
Molecular Hydrogen’s Role in Reducing Oxidative Stress
Anti-oxidation is the process that prevents the increase of active oxygen that necessarily occurs during cell regeneration, or suppresses over activity of active oxygen species. Anti-oxidation substances can naturally occur in the body (SOD, catalase, peroxiredoxin, glutathione) but one can also experience the anti-oxidation effect through stress management, intake of anti-oxidant foods, exercising, or healthy lifestyle.
Antioxidants in the form of supplements, and foods requires that one ingests it which is duly assimilated during the digestion process. Anti-oxidation effect will only show once the product is thoroughly digested, absorbed, and transferred all around the body via blood vessels. The effect will differ based on one’s digestive/absorptive ability, thus anti-oxidant product might not reach a certain area of the body. In patients with lowered metabolic activity, it is even easier to see the oxidation effect.
Molecular Hydrogen inhaled through the nostrils will be absorbed directly into the cells and crosses the Blood Brain Barrier (BBB), which is impermeable to many molecules. However, hydrogen – a nano-molecule – can freely cross the barrier and hence acts as antioxidant, flushing out impurities and damaged cells and ultimately raising the function the immune system.
Medical Hydrogen Gas: Initiation, Development, and Potential of Hydrogen Medicine
H2 rapidly diffuses into tissues and cells, and it is mild enough to neither disturb metabolic redox reactions, nor affect signalling Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS). Owing to its great efficacy and lack of adverse effects, H2 has promising potential for clinical use against many diseases. (Department of Biochemistry and Cell Biology, Institute of Development and Aging sciences, Graduate School of Medicine, Kosugi-machi, April 24th, 2014)
Preventive and therapeutic application of Molecular Hydrogen in situations with excessive production of Free Radicals
Scavenging and cleaning out of free radicals may act preventively or therapeutically. A number of substances that preferentially react with free radicals can serve as scavengers, thus increasing the internal capacity/activity of endogenous antioxidants and protecting cells and tissues against oxidative damage. (Institute for Heart Research, Slovak Academy of Sciences, Bratislava, Slovakia, September 19th, 2016)
Hydrogen gas alleviates oxygen toxicity by reducing hydroxyl radical levels in PC12 cells
Hyperbaric oxygen (HBO) therapy is useful for varieties of clinical conditions, especially hypoxic-ischemic diseases. However, because of generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), breathing oxygen gas at high pressures can cause oxygen toxicity in the Central Nervous System, leading to multiple neurological dysfunctions, which limits the efficacy of HBO Therapy. Studies have shown that Hydrogen gas (H2) can diminish oxidative stress and effectively reduce Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) associated with diseases.
Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic Antioxidant by reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals
Persistent oxidative stress is accepted as one of the causes of many common diseases including cancer. This study show that hydrogen (H2) has potential as an Antioxidant in preventive and therapeutic applications. (Department of Biochemistry and Cell biology, Institute of Development and Aging Sciences, Graduate School of Medicine, Japan, May 7th 2007)

